Abstract
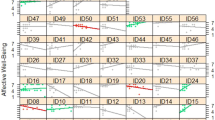
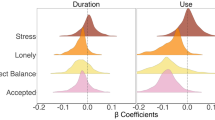
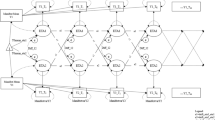
The widespread use of digital technologies by young people has spurred speculation that their regular use negatively impacts psychological well-being. Current empirical evidence supporting this idea is largely based on secondary analyses of large-scale social datasets. Though these datasets provide a valuable resource for highly powered investigations, their many variables and observations are often explored with an analytical flexibility that marks small effects as statistically significant, thereby leading to potential false positives and conflicting results. Here we address these methodological challenges by applying specification curve analysis (SCA) across three large-scale social datasets (total n = 355,358) to rigorously examine correlational evidence for the effects of digital technology on adolescents. The association we find between digital technology use and adolescent well-being is negative but small, explaining at most 0.4% of the variation in well-being. Taking the broader context of the data into account suggests that these effects are too small to warrant policy change.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (YRBS), Monitoring the Future (MTF) and the UK data service (MCS), but restrictions apply regarding the availability of these data, which were used under licence for the current study and so are not publicly available. Data are, however, available from the relevant third-party repository after agreement to their terms of usage. Information about data collection and questionnaires can be found on the OSF website (https://osf.io/7xha2/).
References
Bell, V., Bishop, D. V. M. & Przybylski, A. K. The debate over digital technology and young people. BMJ 351, h3064 (2015).
Children and Parents: Media Use and Attitudes Report. Ofcom https://www.ofcom.org.uk/research-and-data/media-literacy-research/childrens/children-parents-2017 (2017).
Steers, M.-L. N. ‘It’s complicated’: Facebook’s relationship with the need to belong and depression. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 9, 22–26 (2016).
UK Commons Select Committee. Impact of social media and screen-use on young people’s health inquiry launched. Parliament.uk. https://www.parliament.uk/business/committees/committees-a-z/commons-select/science-and-technology-committee/news-parliament-2017/social-media--young-peoples-health-inquiry-launch-17-19/ (2018).
Youth Select Committee. A Body Confident Future (British Youth Council, 2017).
Johnston, L. D., Bachman, J. G., O’Malley, P. M., Schulenberg, J. E. & Miech, R. A. Monitoring the future: a continuing study of American Youth (8th- and 10th-Grade Surveys) https://doi.org/10.3886/ICPSR36799.v1 (2016).
Kann, L. et al. Youth risk behavior surveillance – United States, 2015. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 65, 1–174 (2016).
University of London, Institute for Education, Centre for Longitudinal Studies. Millennium Cohort Study: Sixth Survey, 2015 SN: 8156 (2018).
Etchells, P. J., Gage, S. H., Rutherford, A. D. & Munafò, M. R. Prospective investigation of video game use inchildren and subsequent conduct disorder and depression using data from the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children. PLoS One 11, e0147732 (2016).
Twenge, J. M., Joiner, T. E., Rogers, M. L. & Martin, G. N. Increases in depressive symptoms, suicide-related outcomes, and suicide rates among U.S. adolescents after 2010 and links to increased new media screen-time. Clin. Psychol. Sci. 6, 3–17 (2017).
Parkes, A., Sweeting, H., Wight, D. & Henderson, M. Do television and electronic games predict children’s psychosocial adjustment? Longitudinal research using the UK Millennium Cohort Study. Arch. Dis. Child. 98, 341–348 (2013).
Ferguson, C. J. The problem of false positives and false negatives in violent video game experiments. Int. J. Law Psychiatry 56, 35–43 (2018).
Przybylski, A. K. & Weinstein, N. A large-scale test of the Goldilocks hypothesis. Psychol. Sci. 28, 204–215 (2017).
Ferguson, C. J. Everything in moderation: moderate use of screens unassociated with child behavior problems. Psychiatr. Q. 88, 797–805 (2017).
What About Youth Study. NHS Digital (National Health Service, 2017).
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Health Resources and Services Administration, Maternal and Child Health Bureau. Child Health USA 2014 (U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 2015).
Livingstone, S., Haddon, L., Görzig, A. & Ólafsson, K. Technical Report and User Guide: The 2010 EU Kids Online Survey (EU Kids Online, 2011).
Silberzahn, R. et al. Many analysts, one data set: making transparent how variations in analytic choices affect results. Adv. Method Pract. Psychol. Sci. 1, 337–356 (2018).
Gelman, A. & Loken, E. The garden of forking paths: why multiple comparisons can be a problem, even when there is no “fishing expedition” or “p-hacking” and the research hypothesis was posited ahead of time. Psychol. Bull. 140, 1272–1280 (2014).
Simmons, J. P., Nelson, L. D. & Simonsohn, U. False-positive psychology: undisclosed flexibility in data collection and analysis allows presenting anything as significant. Psychol. Sci. 22, 1359–1366 (2011).
Marszalek, J. M., Barber, C., Kohlhart, J. & Cooper, B. H. Sample size in psychological research over the past 30 years. Percept. Mot. Skills 112, 331–348 (2011).
Chambers, C. D. Registered reports: a new publishing initiative at Cortex. Cortex 49, 609–610 (2013).
Munafò, M. R. et al. A manifesto for reproducible science. Nat. Hum. Behav. 1, 0021 (2017).
Van’t Veer, A. E. Pre-registration in social psychology—a discussion and suggested template. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 67, 2–12 (2016).
Simonsohn, U., Simmons, J. P. & Nelson, L. D. Specification curve: descriptive and inferential statistics on all reasonable specifications. SSRN Electron. J. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2694998 (2015).
Rohrer, J. M., Egloff, B. & Schmukle, S. C. Probing birth-order effects on narrow traits using specification-curve analysis. Psychol. Sci. 28, 1821–1832 (2017).
Department of Health and Social Care. Matt Hancock Warns Of Dangers Of Social Media On Children’s Mental Health. Gov.uk. https://www.gov.uk/government/news/matt-hancock-warns-of-dangers-of-social-media-on-childrens-mental-health (2018).
Ferguson, C. J. An effect size primer: a guide for clinicians and researchers. Prof. Psychol. Res. Pract. 40, 532–538 (2009).
Lakens, D. & Evers, E. R. K. Sailing from the seas of chaos into the corridor of stability: practical recommendations to increase the informational value of studies. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 9, 278–292 (2014).
Scharkow, M. The accuracy of self-reported Internet use—a validation study using client log data. Commun. Methods Meas. 10, 13–27 (2016).
Twenge, J. M., Martin, G. N. & Campbell, W. K. Decreases in psychological well-being among American adolescents after 2012 and links to screen-time during the rise of smartphone technology. Emotion https://doi.org/10.1037/emo0000403 (2018).
Maslowsky, J., Schulenberg, J. & Zucker, R. Influence of conduct problems and depressive symptomatology on adolescent substance use: developmentally proximal versus distal effects. Dev. Psychol. 40, 1179–1189 (2014).
Robins, R. W., Hendin, H. M. & Trzesniewski, K. H. Measuring global self-esteem: construct validation of a single-item measure and the Rosenburg self-esteem scale. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 27, 151–161 (2001).
Angold, A., Costello, E. J., Messer, S. C. & Pickles, A. Development of a short questionnaire for use in epidemiological studies of depression in children and adolescents. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 5, 237–249 (1995).
Goodman, R., Ford, T., Simmons, H., Gatward, R. & Meltzer, H. Using the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) to screen for child psychiatric disorders in a community sample. Br. J. Psychiatry 177, 534–539 (2000).
Goodman, R. Psychometric properties of the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 40, 1337–1345 (2001).
Desai, S., Chase-Lansdale, P. L. & Michael, R. T. Mother or market? Effects of maternal employment on theintellectual ability of 4-year-old children. Demography 26, 545 (1989).
Kiernan, K. E. & Mensah, F. K. Poverty, maternal depression, family status and children’s cognitive andbehavioural development in early childhood: a longitudinal study. J. Soc. Policy 38, 569 (2009).
Mensah, F. K., Kiernan, K. E. & Kiernan, K. Maternal general health and children’s cognitive development and behaviour in the early years: findings from the Millennium Cohort Study. Child Care Health Dev. 37, 44–54 (2010).
Thomson, E., Hanson, T. L. et al. Family Structure and Child Well-Being: Economic Resources vs. Parental Behaviors. Social Forces 73, 221–242 (1991).
Pople, L. & Sharma, N. Factors Affecting Children’s Mental Health over Time (The Children’s Society & Barnardo’s, 2018).
Cadman, D., Boyle, M., Szatmari, P. & Offord, D. R. Chronic illness, disability, and mental and social well-being: findings of the Ontario Child Health Study. Pediatrics 79, 805–813 (1987).
Acknowledgements
The National Institute on Drug Abuse provided funding for the MTF conducted at the Survey Research Centre in the Institute for Social Research, University of Michigan. The YRBS was collected by the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention. The Centre for Longitudinal Studies, UCL Institute of Education collected the MCS and the UK Data Archive/UK Data Service provided the data. They bear no responsibility for its aggregation, analysis or interpretation. A.O. was supported by a EU Horizon 2020 IBSEN grant. A.K.P. was supported by an Understanding Society Policy Fellowship funded by the Economic and Social Research Council. A.O. and A.K.P.’s funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript. Thanks are extended to U. Simonsohn, N.K. Reimer and N. Weinstein for their valuable input, and to J.M. Rohrer, U. Simonsohn, J.P. Simmons and L.D. Nelson for code provision. We also acknowledge the use of the University of Oxford Advanced Research Computing facility in carrying out this research: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.22558. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.O. conceptualized the study, with regular guidance from A.K.P. A.O. completed the statistical analyses and drafted the manuscript. A.K.P. gave integral feedback in the process.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
A.O. has no competing interests. A.K.P. has no competing financial interests; in the last five years A.K.P. has served in an unpaid advisory capacity with the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, Facebook Inc., Google Inc. and the ParentZone.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Methods, Supplementary Figures 1–12, Supplementary Tables 1, 2, 5, 6, Supplementary Note, and Supplementary References
Supplementary Table 3
The MTF questionnaire contains different questionnaire types that are completed by different subsets of participants. Different numbers of participants, therefore, completed different combinations of questions, the details of which are displayed in this table. DS, depressive symptoms, SE, self-esteem; LO, loneliness.
Supplementary Table 4
In both the MTF and YRBS datasets questions were added and changed over the course of the study. This table outlines these alterations, showing both when questions were added and when they were modified.
Supplementary Software
R code and .run scripts to reproduce the analyses presented in the manuscript. A life version of this code can be found on the Open Science Framework: https://osf.io/e84xu/.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orben, A., Przybylski, A.K. The association between adolescent well-being and digital technology use. Nat Hum Behav 3, 173–182 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-018-0506-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-018-0506-1